DevOps is an approach to software delivery that is used in the context of agile/lean software development approaches, primarily for constructing systems of engagement such as online and mobile banking applications. DevOps technologies include application deployment automation and release coordination, and is frequently associated with cloud computing and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
DevOps is a required technology capability that supports the agile delivery of new services business capability.
An example DevOps offering in the cloud is IBM’s Bluemix.
DevOps for Dummies provides the following DevOps reference architecture:
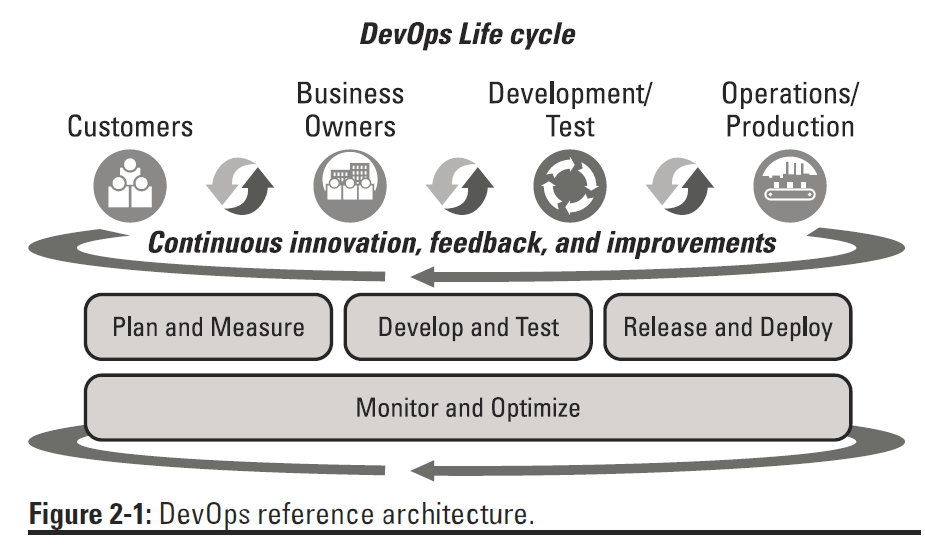
Plan and Measure involves the practice of continuous business planning and benefits from DevOps due to the frequent customer feedback possible from the smaller, more frequent releases in continuous delivery.
Develop and Test involves collaborative development and continuous testing. Collaborative development is the whole agile development space with its inclusion of a broad spectrum of participants, continuous integration, etc. Continuous testing goes beyond earlier manual testing to include test automation and simulation (i.e. service virtualization with GreenHat, etc).
Release and Deploy involves application deployment automation and release coordination, expands continuous integration into continuous delivery to QA and production, and establishes a delivery pipeline.
Monitor and Optimize involves continuous monitoring, both of the operational environment and customer behavior for the purpose of creating a rich and timely feedback loop.
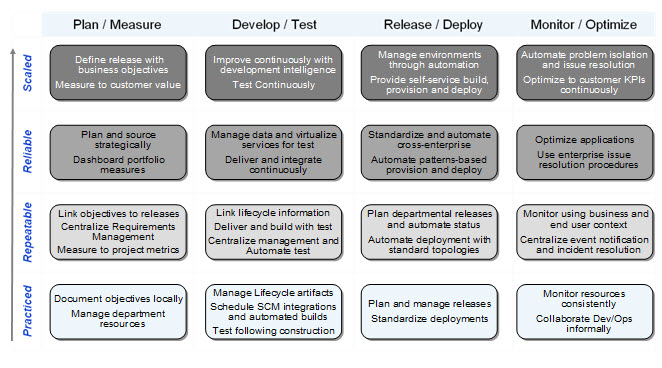
DevOps Maturity Model
IBM provides a DevOps Maturity Model to help with assessment.
Like this:
Like Loading...

