Responsive design is the practice of designing mobile applications such that they are displayed appropriately on different form factors. Responsive designs have a layout based upon percentages as opposed to numbers of pixels, and leverages enabling technologies such as fluid grids (formatting into columns) and media queries (CSS selection based upon device and orientation).
Monthly Archives: July 2014
IT Capability: Agile Development and Continuous Delivery
Agile application development and continuous delivery are IT capabilities that allow project teams to respond to changing requirements resulting from a changing environment and insights, and release functional enhancements in rapid succession, whether it be to a formal test organization or production. Agile development supports continuous delivery. When I think of agile development I think about SCRUM as a project approach and supporting extreme programming techniques such as continuous integration, refactoring, and test-first design.
IT Capabilities: What Are They?
Capabilities are “Ability to…” statements that state the strategic requirements of an organization. I see them as existing within the organization’s strategy. Businesses require business capabilities such as the “Ability to protect client information”. These are supported by people, process and technology enablers. Enablers describe how the organization realizes these capabilities.
IT Capabilities are service capabilities within the IT group of the business. These are analogous to business capabilities, but are derived from strategic technologies. If a company needs an application scanning and testing technology to support the ability to protect client information, then they will also need people, processes and possibly even additional technology to support that technology.
IT capabilities are important to track as they must be built out as part of transformation projects.
Strategic Technology: Customer Experience Management (IBM TeaLeaf)
Gaining visibility to the quality of experience of customers and other users when using mobile and Web applications is an important step in learning about customers. Looking for excessive device rotations, zooms, abandonment, etc. can help identify and diagnose design weaknesses in applications so that they may be corrected before they spoil the experience of too many customers.
TeaLeaf is an IBM product that provides the Customer Experience Management (CEM) capability. For Web apps TeaLeaf scans HTTP traffic and provides a DOM listener. For native apps a library is compiled into the app.
CEM is a subset of CRM capability that is often of interest to marketing and customer support strategists.
Strategic Technology: DevOps (Bluemix)
DevOps is an approach to software delivery that is used in the context of agile/lean software development approaches, primarily for constructing systems of engagement such as online and mobile banking applications. DevOps technologies include application deployment automation and release coordination, and is frequently associated with cloud computing and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
DevOps is a required technology capability that supports the agile delivery of new services business capability.
An example DevOps offering in the cloud is IBM’s Bluemix.
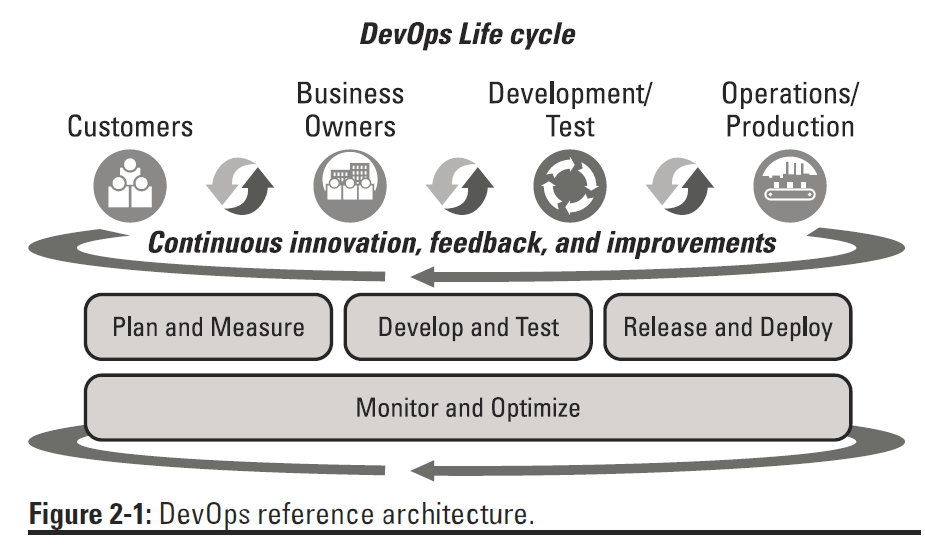
DevOps for Dummies provides the following DevOps reference architecture:
Plan and Measure involves the practice of continuous business planning and benefits from DevOps due to the frequent customer feedback possible from the smaller, more frequent releases in continuous delivery.
Develop and Test involves collaborative development and continuous testing. Collaborative development is the whole agile development space with its inclusion of a broad spectrum of participants, continuous integration, etc. Continuous testing goes beyond earlier manual testing to include test automation and simulation (i.e. service virtualization with GreenHat, etc).
Release and Deploy involves application deployment automation and release coordination, expands continuous integration into continuous delivery to QA and production, and establishes a delivery pipeline.
Monitor and Optimize involves continuous monitoring, both of the operational environment and customer behavior for the purpose of creating a rich and timely feedback loop.
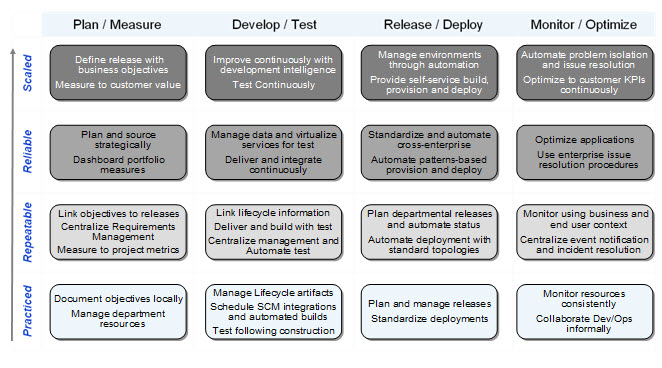
DevOps Maturity Model
IBM provides a DevOps Maturity Model to help with assessment.
Strategic Technology: Streams (IBM BigInsights)
Stream processing, or the real-time processing of big data in motion, is an IBM technology growing, as far as I know, out of big data processing systems developed for the US intelligence agencies years ago.
The IBM product providing this capability is BigInsights.
Strategic Technology: Content Analytics (IBM ECM)
Content analytics scans unstructured data such as text in social media, call center databases and emails, performs natural language processing to understand the meaning of the data, and reports the results.
IBM Enterprise Content Manager (ECM) contains content analytics functionality.
Strategic Technology: NoSQL
Strategic Technology: Hadoop (IBM BigInsights)
Apache Hadoop is open source software which allows storage, retrieval and computations on at-rest big data using commodity hardware and infrastructure. Hadoop includes the distributed file system (HDFS) and MapReduce programming model.
Hadoop addressed the strategic technology capability to process at-rest big data.
IBM provides InfoSphere BigInsights that is based upon Hadoop.
BigInsights also addresses strategic technology capabilities:
- Process streaming big data in real time
- Discover enterprise data across multiple data sources.
Strategic Technologies: What are they?
Strategic technologies are technologies which are called out in the IT strategy as being key enablers to the business strategy. During the environment scan trends and forces are studied, and threats and opportunities are identified. The strategy is crafted to respond to threats and opportunities by adding or removing strategic business capabilities. Some new business capabilities will depend upon new technologies, and using new technologies typically requires new IT capabilities such as the ability to develop with and operate the technologies. All of this is graphed in a strategic capability network (SCN).
This series does not build an SCN, but simply contains an inventory of strategic technologies which I will refer to later when I illustrate typical SCN patterns for banks.